Redhat Process Automation Manager for Business Architects
 Red Hat Process Automation Manager
Red Hat Process Automation Managerfor Business ArchitectsMaster the art of modeling business solutions
 Practical Hands on Labs.
Practical Hands on Labs.Many labs with hands on experience; practicing real challenging exercises
independently and supervised by your professional trainer Earn your recognition
Earn your recognitionBe part of the professional world, standout for your proven knowledge and skills
 Live Demos! .
Live Demos! .With visual view of how the concepts can be realized using live data
and live practices by the instructor.
Thanks to the training Kata where the instructor leads and students
follow instructions step by step

IBM-10114
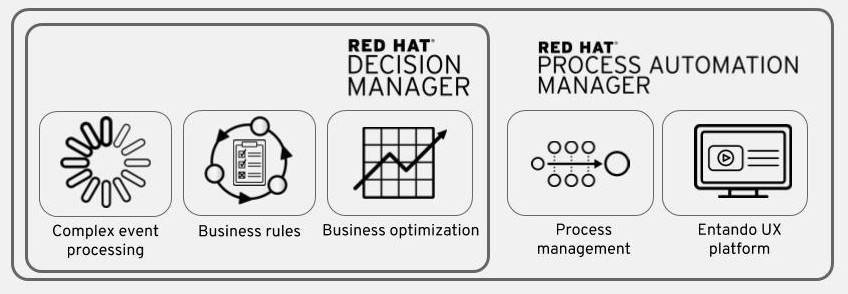
Red Hat® Process Automation Manager is a comprehensive platform for business process management that can be deployed across multiple cloud environments.

Overivew
Throughout this course, students will learn the basics of Process and Decision making specialized to business architects.
As a developer of business decisions and processes , you can use Red Hat Process Automation Manager to develop decision services and process services using a variety of available assets. You can also use Red Hat build of OptaPlanner to find the optimal solution to planning problems based on a set of limited resources and under specific constraints.
Prerequisites
Knowledge
Students to this class are expected to have:
- Good understanding Business Analysis is preferrable
- Good understanding of business vertical on specific industry
- Basic skills of structuring information, gather information, and facilitating workshops
- Basic understanding of computer operations skills :such as managing files, and browsing through applications
Technology
Depending on the delivery method of this course, the students should have :
- A Workstation with Internet browser capability such as (Chrome, Edge, or Safari)
- Good persistent internet connection without blocking firewalls(ideally non corporate firewall protected workstations)
The Labs
Labs are provided throughout the course
Labs covered in this course:
- Lab 1: Create a project in Business Central
- Lab 2: Design BPM Business Case Mortgage approval
- Lab 3: Interactive Process Approval
- Lab 4: DMN Business Case Traffic Violation
- Lab 5: Decision Tables and Boxed Expressions
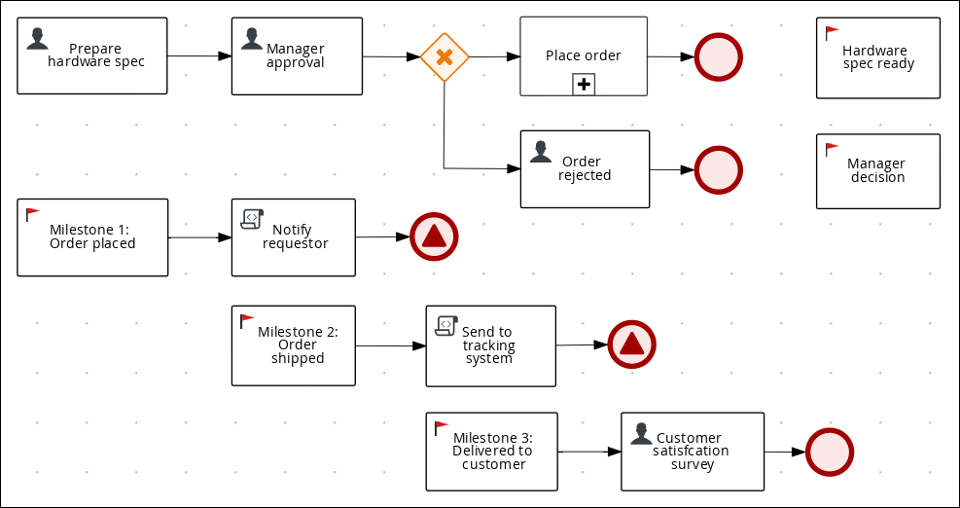
- Lab 6: Order Processing Case
- Lab 7: Order Processing Case with milestones
- Lab 8: Deploy and Execute models
Objectives
By the end of the course, students should be able to
-
Understand Business Architecture role and strategic alignment
-
Identify and describe the main components of Red Had Process Automation Manager
-
Describe the different Modeling languages
-
Develop and Maintain Business Process and Decision Models on Red Hat Process Automation Manager
-
Manage the development lifecycle of Processes within Red Hat PAM
Audience
This course is designed to assist and equip the students with the skills and knowledge at the development hands on level, that allow them to perfect their daily tasks with respect to modeling business processes and automate decision making process, these are examples of the beneficiary audiences of the course.
- Business Architects: Help the Business Architect model, test, and maintain business models and decision making processes as workflows to the business practice
- Business Analysts: Be able to fine tune and test and review business models, validate and assist software developers understand the business modeling and decision making practice
- Product owners: Understand the business impact and importance of modeling BPMN, and DPM Decision Process Modeling to enhance improve business practices for agility and effectivness
- DevOps Developers: As full stack developers, be part of the modeling team to gather and model business practicess into effective workflows
- DevOps Engineers: to understand how to fit the development and deployment of Red Hat Process Automation Manager models effectively into the CI/CD pipelines
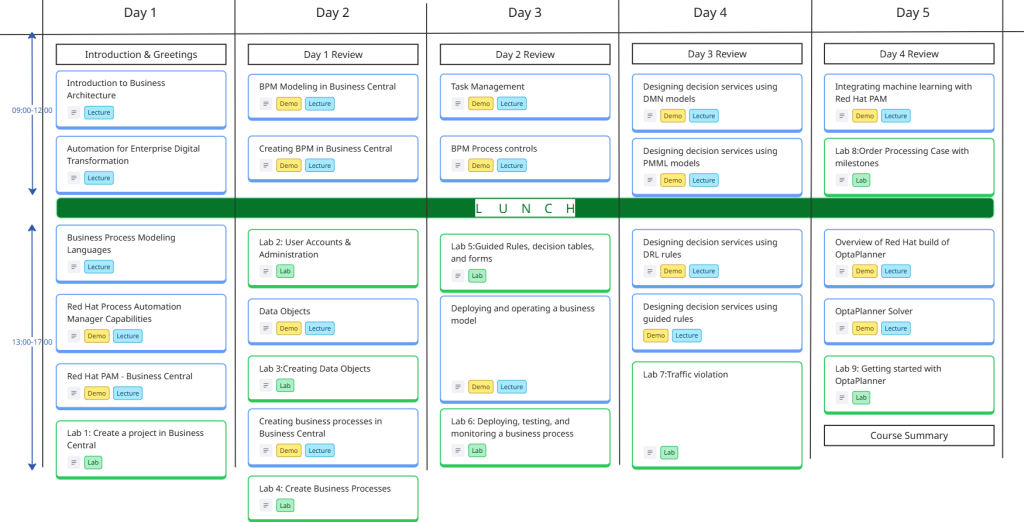
Timeline
The Red Hat Process Automation Manager for Business Architects Course is a 5 days course, includes lectures, demos, and workshops.
The following is guidelines for the instructor to organize the time pace with the students, subject to change based on students preference.
Breaks during the day follows the 106 rule, every 45-60m
*the 106 rule, indicates the human memory capacity to learn the new factual elements which is 106 facts before the memory could be reused.
Course Curriculum
Module 1: Introduction to Business Architecture
- Holistic View
- Strategy Alignment
- Process Optimization
- Agility
- Common Languate
Module 2: Automation for Enterprise Digital Transformation
- Automation Defined
- Adoption Strategies
- Pre-requisites to automation journey
- Automation Use Cases
- Types of Automation
- 5-STeps to automate a process
Module 3: Business Process Modeling Languages
- Overview of Business Process Modeling
- Business Process Modeling Techniques
- BPMN Business Process Modeling Notation
- BPEL Business Process Expression Languate
- Modeling UML-Use Cases
- Business Scenarios technique
- Value Stream Management VSM
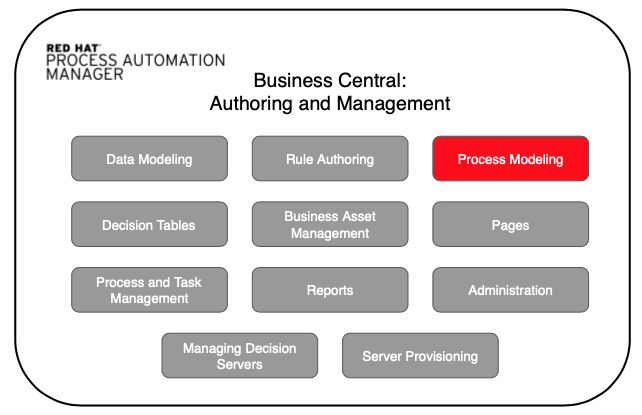
Module 4: Red Hat Automation Manager Components
- Components of Red Hat Process Automation Manager
- Business Central
- KIE Execution Engine
- Git Repository
- Maven Build
Module 5: The Business Central Structure
- Overview of Red Hat Business Central in PAM
- Spaces
- Projects
- Assets
- Data Objects
Module 6: BPM Modeling using Business Central
- BPMN Business Process Modeling Notation
- Getting Started with Business Central User Interface
- Process Events
- Data Objects
- Connections
- Tasks
Module 7: BPM Modeling Business Process Approval
- Validating a process
- Outgoing Connections
- Validating Data
- Calculating Values
- Process Approval
Module 8: Modeling Guided Rules
- Defining Business Rules
- Guided Rules conditions
- Error Conditions and Validation Error Data-Object
- Guided Decision Tables
Module 9: Interactive Forms
- Use cases of interactive forms
- Generating Automatic Forms
- Editing Forms
Module 10: Developing Decision Models
- DMN Decision requirements Diagram
- FEEL rule expressions
- DMN Boxed expressions
- DMN Business Workshop
Module 11: Data Types in FEEL
- Numbers
- Strings
- Boolean values
- Dates
- Time
- Date and time
- Days and time duration
- Years and months duration
- Functions
- Contexts
- Ranges (or intervals)
- Lists
Module 12: Functions and Expressions
- Overview of Functions Categories
- Conversion Functions
- Boolean Functions
- String Functions
- List Functions with Loop statement
- Numeric Functions
- Date and Time Functions
- Range Functions
- Temporal Functions
- Sort Functions
- Context Functions
Module 13: DMN Decision Tables
- Overview of Decision Tables
- Business uses of Decision Tables
- Hit Policies
Module 14: DMN Boxed Expressions
- Boxed Literals
- Boxed Content
- Boxed Relation
- Boxed Expression
- Boxed Invocation expressions
- Boxed List expressions
Module 15: Business Process Case Management
- Overview of case management in Red Hat Process Automation Manager
- Project of Case Management
- Data Objects for Case Management
- Survery Data Objects for Case Management
- Designing the case definition
Module 16: Drill down with Sub-processes
- Resolving Process complexity with sub-processing
- Create sup Processes
Module 17: Manager Approval Business Processes
- Process optimization to reduce human interaction
- Creating Manager Approval processes
Module 18: Working with Milestones
- Identify different types of milestones
- Manager Decision Milestone
- Process Task Milestone
- Termination Milestone
Module 19: Opta Planner
- Introduction to Redhat build of OptaPlanner
- Examples of OptaPlanner
- OptaPlanner with Business Central
Module 20: Manage Model Development Lifecycle
- Phases of Model Development Lifecycle
- Project Versioning with Git
- Project Building with Maven
Module 21: Deploying, executing, and monitor Business Models
- Test and deploy Business Process Models
- Test and deploy Business Decision Models
- Test and deploy Business Cases
- Monitor performance
- Troubleshooting
Calendar
Scroll through the months, and chose the right schedule for you, send us a standard request form register